| [1] Balamuthusamy S, Kosla S, Benatar D, et al. Myocardial infarction in a young African-American male due to myocardial bridging. Cardiology. 2006;105:165-167.[2] Yetman AT, McCrindle BW, MacDonald C, et al. Myocardial bridging in children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy-a risk factor for sudden death. N Engl J MeO.1998;339: 1201-1209.[3] Channer KS,Bukis E,Hartnell G,et al.Myocardial bridging of the coronary arteries. Clin Radiol.1989;40:355-359.[4] Hansen BF.Myocardial covering on epicardial coronary arteries,prevalence, localization and significance. Scand J Thor Cardiovasc Surg.1982;16:151-155.[5] 张国辉.心肌桥对冠状动脉粥样硬化和血流的影响[D].上海:复旦大学,2002.[6] Alegria JR, Herrmann J, Holmes DR, et al.Myocardial bridging. Eur Heart J. 2005;26:1159-1168.[7] 徐时.心肌桥形态学观测及相关因素分析的研究[D].甘肃:兰州大学,2009.[8] Ishii T, Asuwa N, Msuwa N, et al. The effects of a myocardial bridge on coronary atherosclerosis and is chaemia. J Pathol. 1998;185:4-9.[9] Ishii T, Hosdoa Y. The significance of myocardial bridge upon atherosclerosis in the left anterior descending coronary artery.J Pathol.1986;148:279-291.[10] 张国辉,葛均波.心肌桥的临床研究现状[J].中国介入心脏病杂志,2002,10(1):31-33.[11] Chiu JJ, Wang DL, Chien S, et al. Effects of disturbed flow on endothelial cells.J Biomech Eng.1998;120:2-8.[12] Rosencrance G, Deer TR, Lee KC, et al. Coronary artery muscle bridging causing class III angina in a patient with no coronary atherosclerosis. W V Med J.1995;91:1967.[13] 郑志敏,徐根林,李维俭,等.心肌桥对冠状动脉血流量的影响[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2006,26(2):166-168.[14] Warboys CM, Amini N, De Luca A, et al. The role of blood flow in determining the sites of atherosclerotic plaques. F1000 Med Rep.2011;3:5.[15] Woo KV, Qu X, Babaev VR,et al.Tiel attenuation reduces murine atherosclerosis in a dose-dependent and shear stress-specific manner.J Clin Ivest.2011;121(4):1642-1635.[16] Ravenbergen J,Ravensbergen JW,Krijger JK,et al. Localizing role of hemodynamics in atherosclerosis in several human vertebrobasilar junction geometrics. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.1998;18(5):708-716.[17] 杨永宗.动脉粥样硬化性心血管病基础与临床[M].北京:科学出版社,2009.537-551.[18] Pan S.Molecular mechanisnis responsible for the atheroprotective effects of laminar shear stress.Antioxid Redox Signal.2009;11(7):1669-1682.[19] Noble J, Bourassa MG, Pettclerdc R, et al. Myocardial bridging and milk effect of the left anterior descending artery: normal variant or obstruction?. Am J Cardiol.1976;37:993- 999.[20] 柳兆荣,何烽,徐刚,等.动脉管壁切应力的确定[J].中国科学(A辑), 2001,31(7):651-660.[21] 刘宝玉,柳兆荣.刚性圆管中血液周期振荡流的切应力分布[J].力学季刊,2002, 23(3):7-8.[22] 扬俊,郭涛.血液黏度正常值探讨[J].中国血液流变学杂志, 1998, 8(1):69.[23] 姚泰,吴博威.生理学[M].6版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2003: 93-104.[24] 张国辉,葛均波,沈力行,等.心肌桥-壁冠状动脉血液动力学模型的设计和制作[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2005:22(3):593-597.[25] 谭荣波,梅晓仁.SPSS统计分析实用教程[M].北京:科学出版社, 2007:82-97.[26] 顾兴华,王华,王克强,等.切应力对内皮细胞膜流动性的影响[J].解剖学杂志,2000,23(4):352-354.[27] 王华,王克强,贾建国,等.切应力对内皮细胞膜微粘度的影响[J].上海生物医学工程,2001,22(3):61-62,26.[28] 秦海强,赵性泉,周萍,等.血压和心率对颈动脉管壁切应力影响的初步研究[J].中国卒中杂志,2012,7(6):461-465.[29] 牛静,戴璇,乔爱科,等.支架置入椎动脉开口处狭窄后突出距离的血流动力学分析[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(6):598-602.[30] 高进涛,王国栋,肖聚亮.缝合式和机械吻合式搭桥模型的血流动力学数值模拟[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报,2012,31(6): 866-874. [31] 王季尧,李文平,王盛章.冠状动脉中氧输运的数值模拟研究[J].生物医学工程学进展,2012,33(3):141-146.[32] 彭红梅,杨德全.腹主动脉叉血流动力学边界元分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2012,29(4):697-700. [33] 丁金立,刘有军,王枫.一种可以避免血管再狭窄的双移植管搭桥方式的数值模拟[J].医用生物力学,2012,(4):432-437.[34] 杨金有,刘静,俞航,等.髂主动脉血栓后与正常髂主动脉血流动力学数值模拟对比分析[J].生物医学工程与临床,2012,16(1): 1-6. [35] 凌生林,张英,廖斌,等.低层流切应力对内皮细胞表面B族Ⅰ型清道夫受体表达的影响[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2009,17(8): 661-664. [36] 王贵学.切应力变化与动脉粥样硬化斑块的形成和破裂[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2009,17(8):625-628. [37] 邢海燕,李宏妹,马丽,等.流体切应力下血管内皮单核细胞趋化蛋白-1的表达[J].中华病理学杂志,2001,30(5):361-364.[38] 王莹,樊瑜波,孙安强.剪切力对动脉血管平滑肌细胞增殖分化的影响[J].生命科学仪器,2008,6(1):31-34.[39] 梁峰,胡大一,王伯瑶,等.切应力诱导人内皮细胞白细胞介素-8基因的转录活化[J].中华内科杂志,2005,44(6):421-424.[40] 唐戎,成敏,聂永梅,等.流体切应力作用强度对内皮细胞IL-8生成的影响[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2004,21(3):363-366.[41] 张文胜,陈槐卿,李良,等.流体切应力强度对内皮细胞IL-8基因表达的影响[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2002,19(2): 181-185, 211.[42] 周瑜,丁皓,徐萌,等.体外细胞培养装置评估交变应力对内皮细胞的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(9):1669- 1671. |
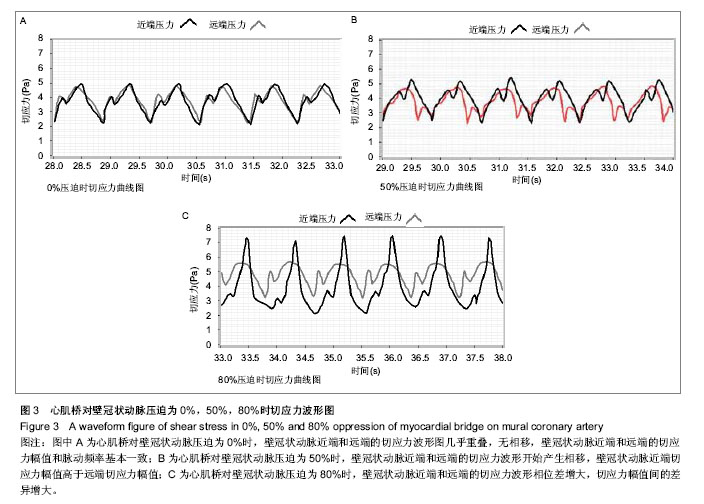
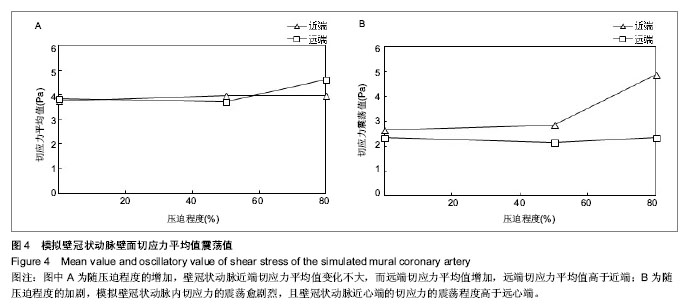
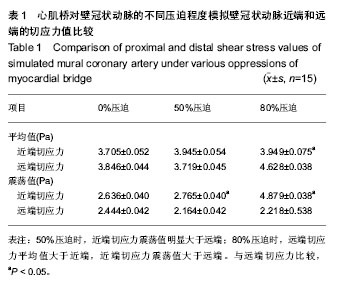
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)